Page V – CASE STUDY
Page V – CASE STUDY: Border Typologies
In order to understand Europe’s external borderlands as well as singularities and similarities between individual regions, one of my iterations included studying one strip of the border in more detail. I started the process of identifying the different parts of the border and what they are characterized by.
When we hear news reports about countries erecting fences along their external borders, we might be under the impression that entire stretches of borderlines are militarized and rendered impenetrable. The reality is different, and by splitting the border into multiple segments, classes or typologies, we can start to learn more about the different processes and experiences they may be producing.
Border of Greece and North Macedonia
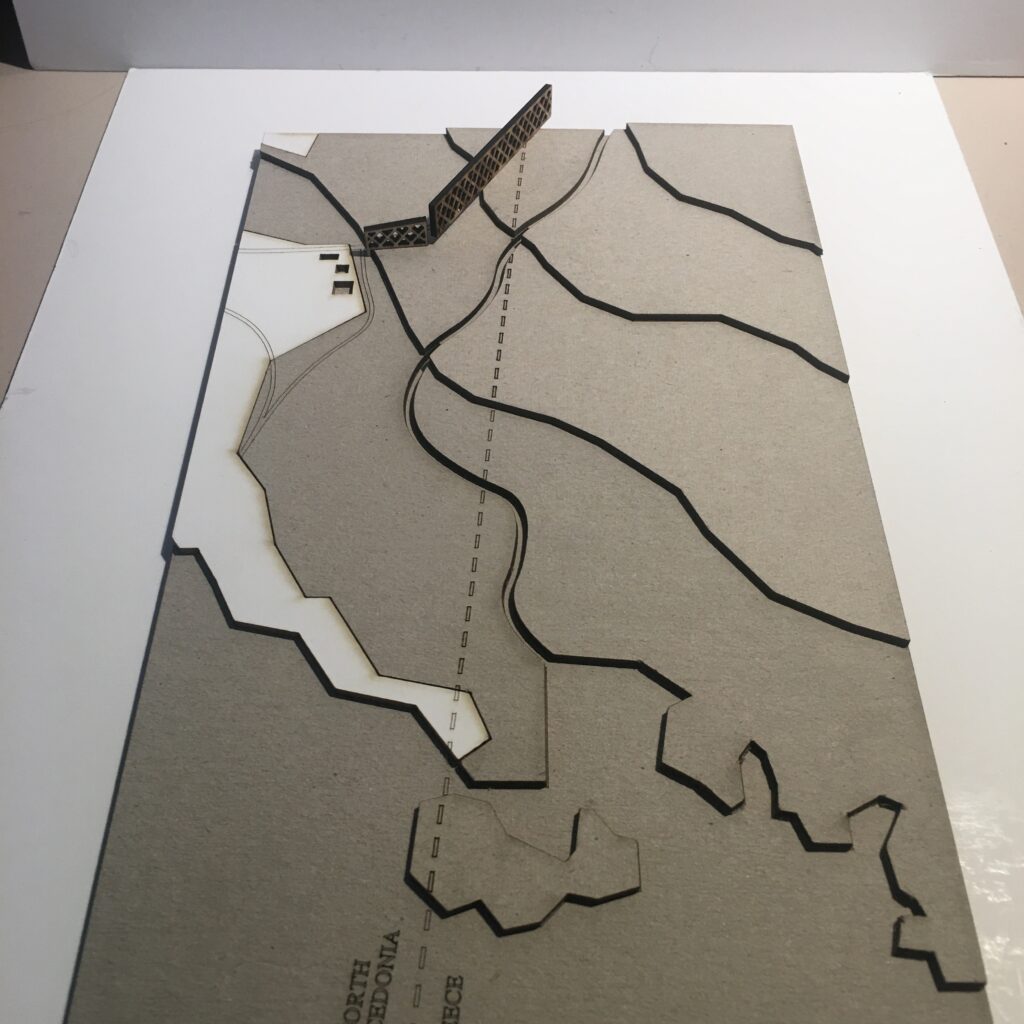
For this iteration I chose to look closer at the border between Greece and North Macedonia. The findings then lay ground for the establishment of four initial border typologies, drawings and models which can be seen further down on this page. The map below is only one portion of the whole, as the full version is too wide to be included in this format.
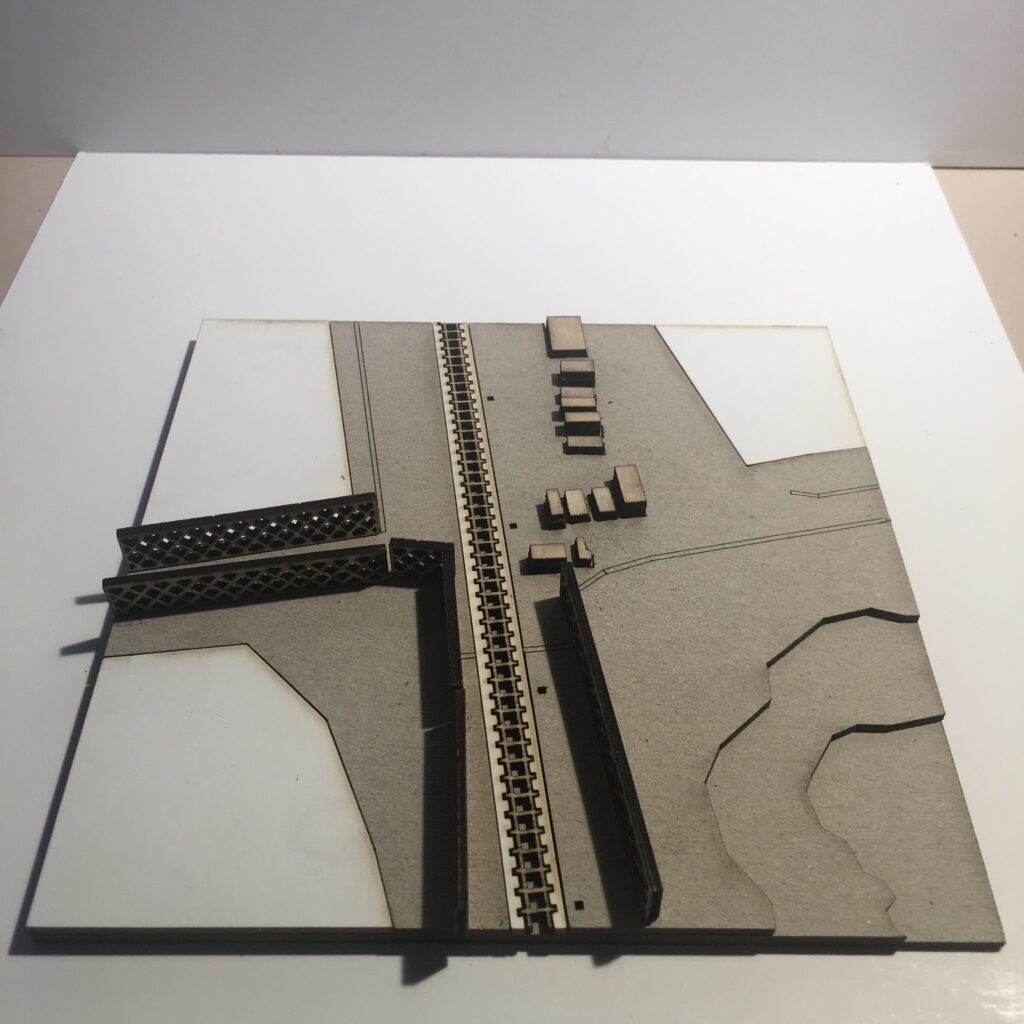
Typology 1: Border at Eidomeni/ Gevgelija
> double fence/rurban/transport infrastructure
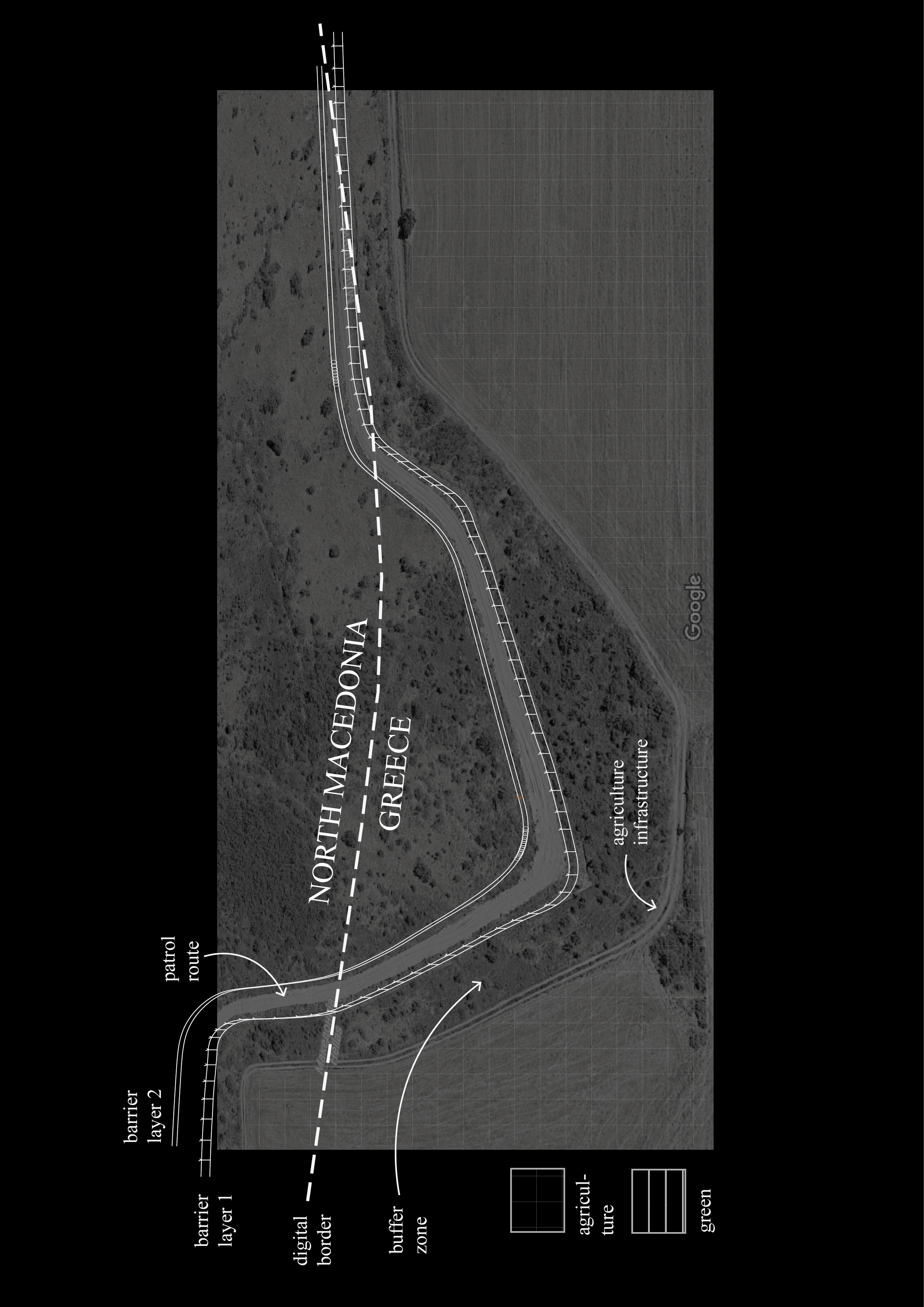
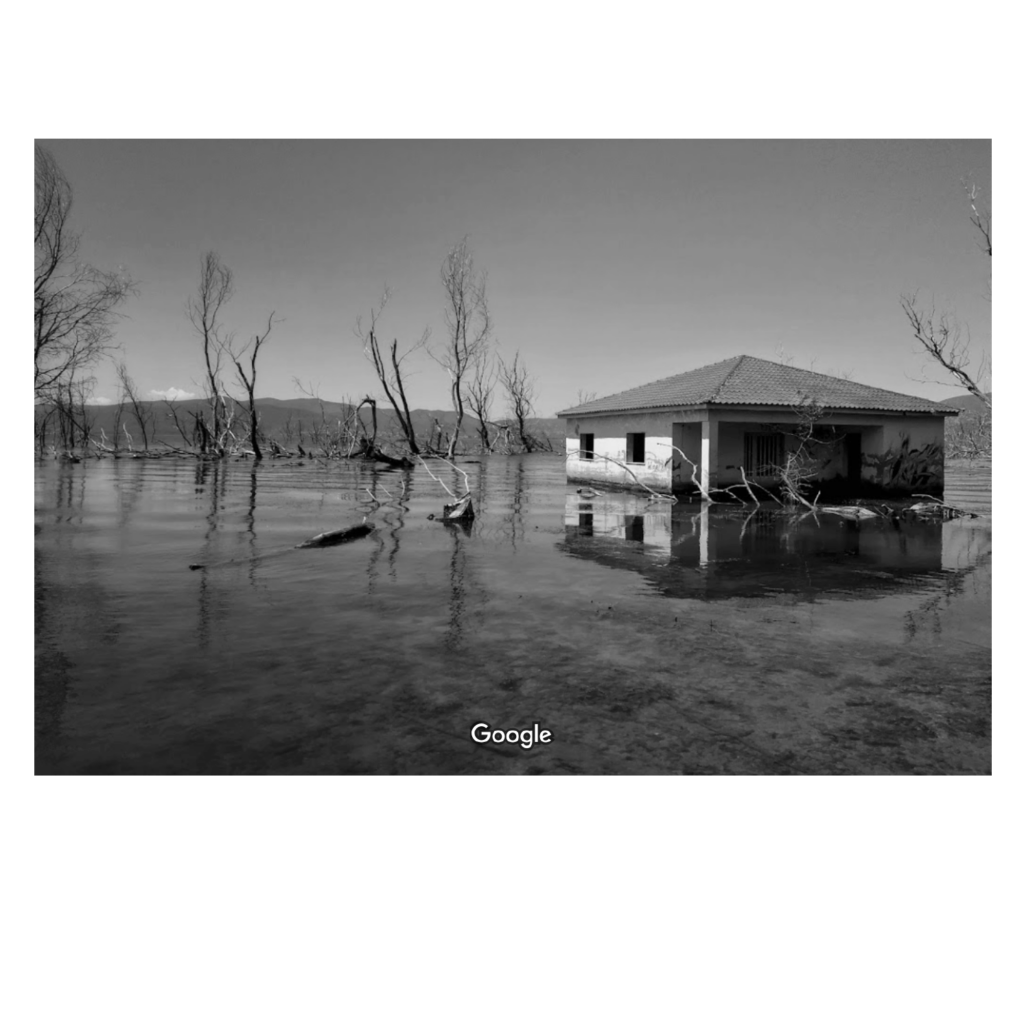
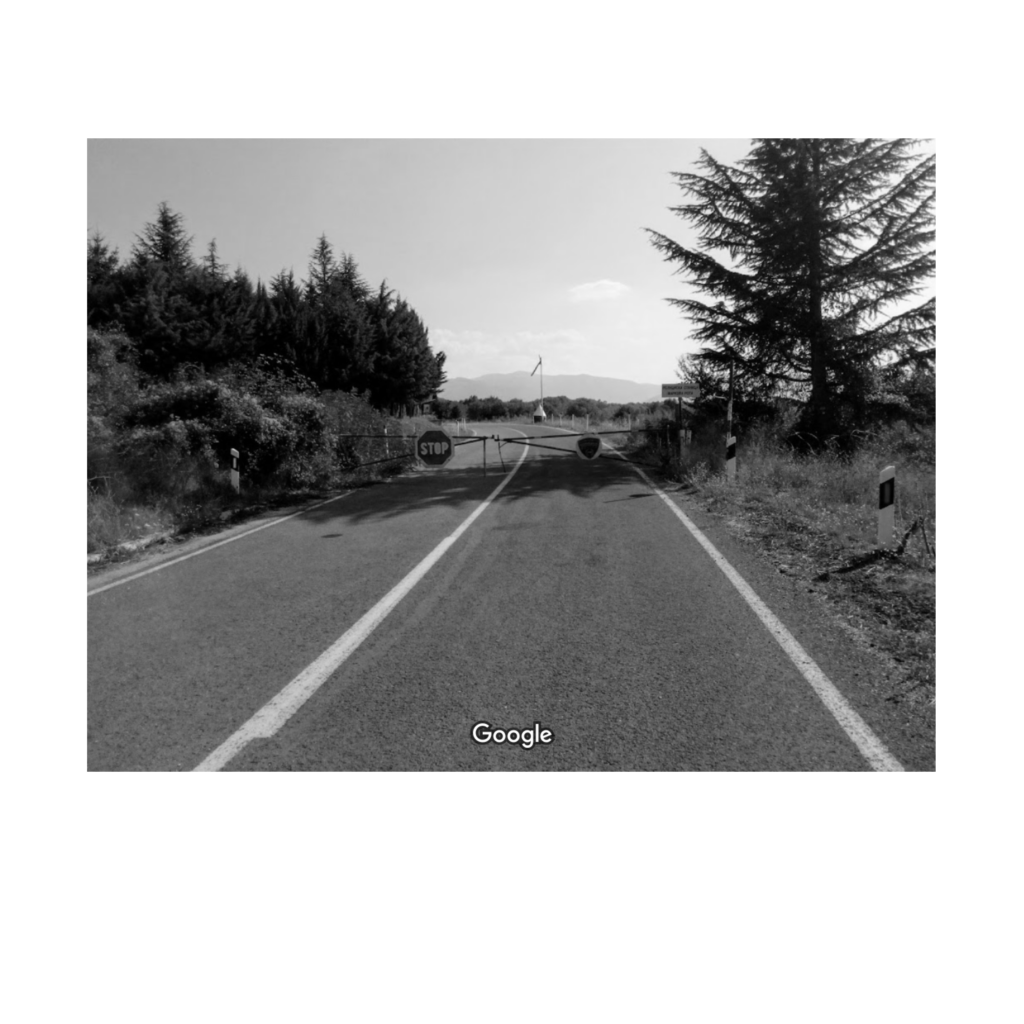
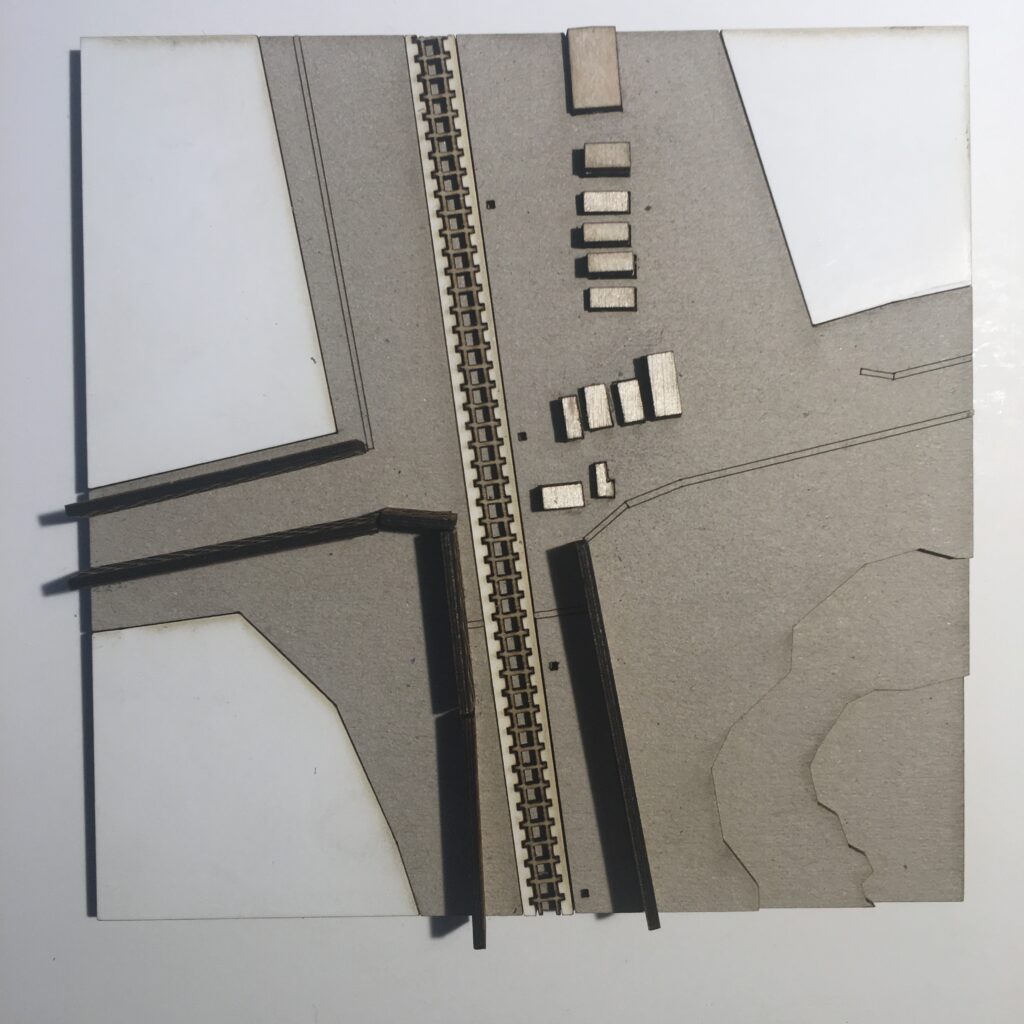
The border region arround the Greek town Idomeni became widely known as being at the epicentre of the European refugee crisis in 2015. Situated right along the western balkan route, the border crossing here gained public intetest when the macedonian government decided to erect a fence on either side of the crossing in November 2015.
Apart from the formal border crossing along the highway, one main point of entry was that of the railroad border crossing a little way west. Images of migrants entering North Macedonia on foot spread internationally, as did the reports of stranded migrants and spontaneous campsites that emerged in the aftermath of the closure of the border.
This border segment is situated in a flat and forgiving landscape, with widespread fields, criss-crossing agricultural paths and roads and multiple towns. The border passes on the outskirts of the larger town of Gevgelija on the Macedonian side, and through crop fields to the south. The only indication of the border (prior to the fence erection in 2015) would have been a shift in crop cultivation.
The border is here characterized by;
> a separation barrier (double fence, barbed wire)
> patrol route
> urban/rural dynamics
Notable to this border crossing is the clear separation between the formal – desired and well integrated border territory, dense with economic activity and cross border exchange – and the informal, humanitarian border crossing. Since the closing of the border in the end of 2015 the amount of migrants crossing the border to North Macedonia on this particular stretch have gone down drastically.
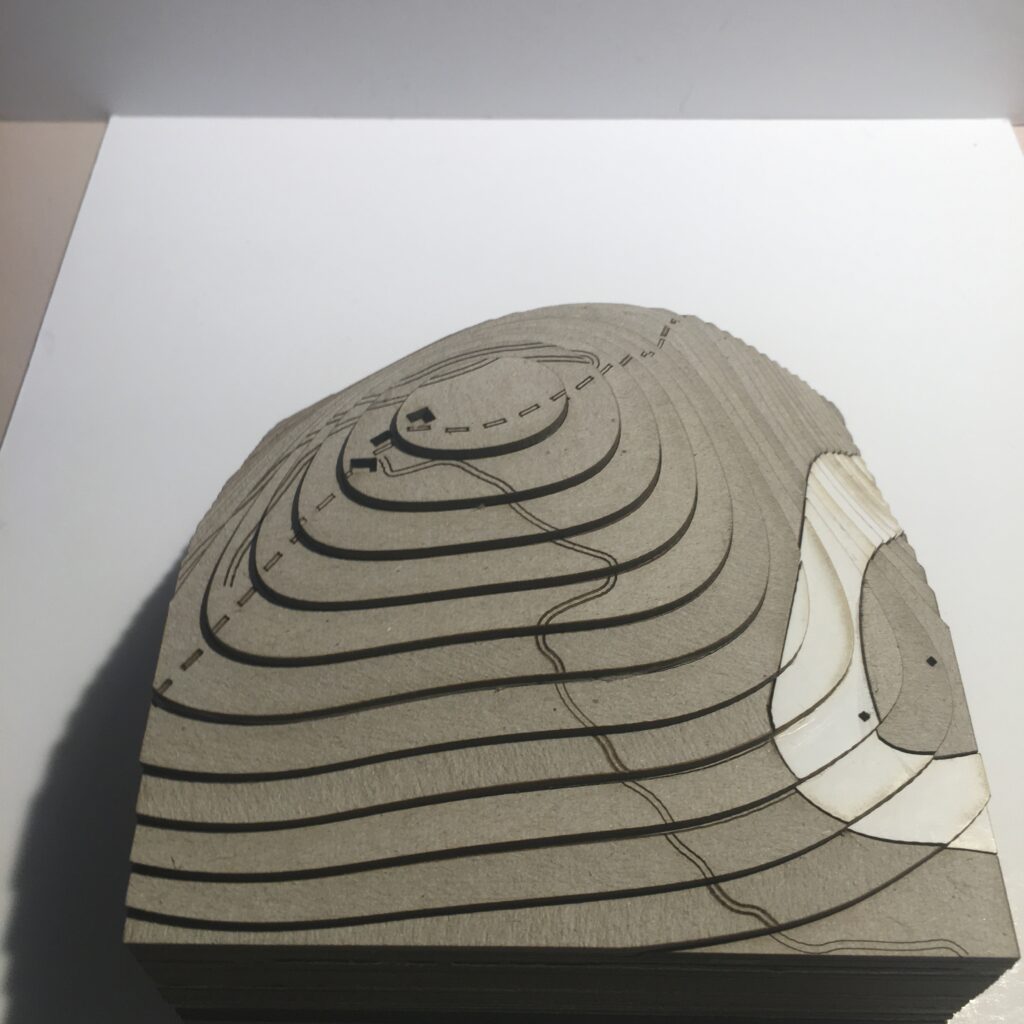
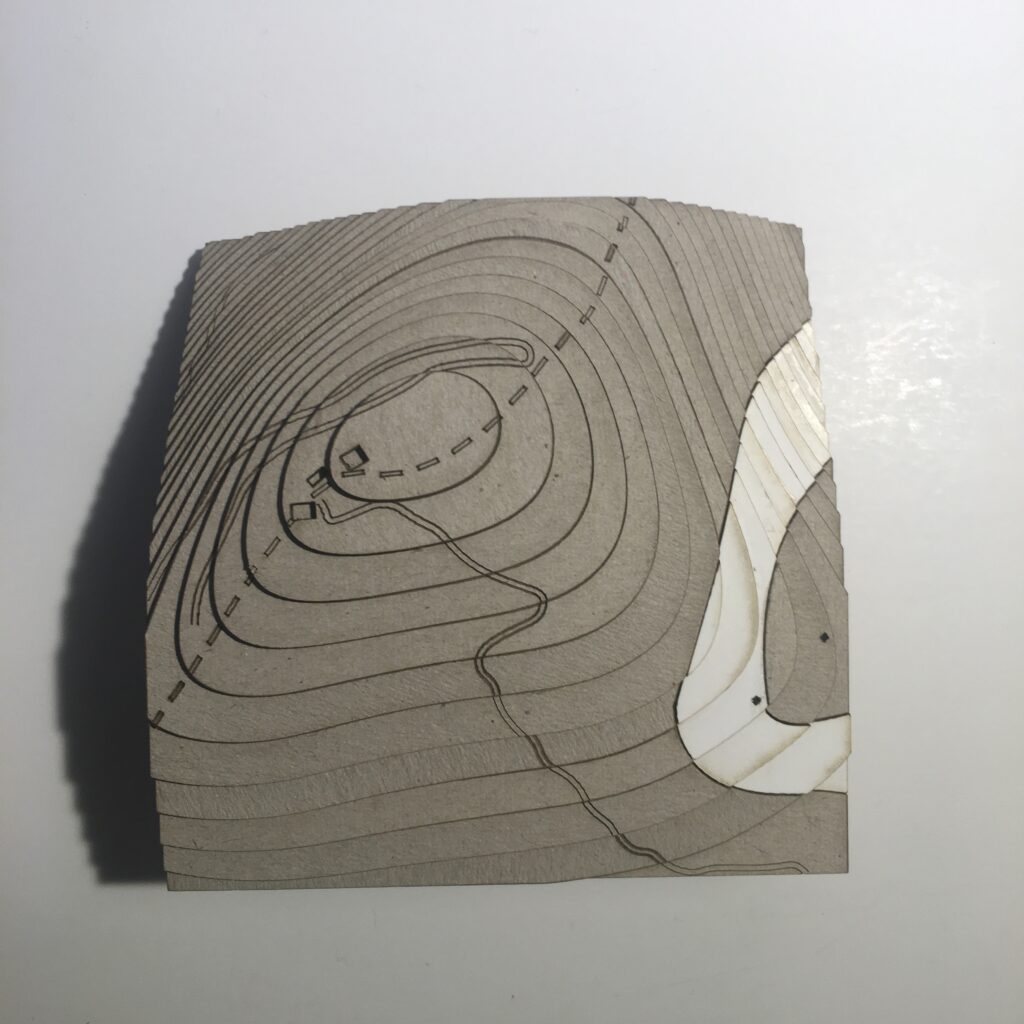
Typology 2: Mt. Kaimaktsalan ski resort
> mountainous/established recreational area
The section of the border is characterized by high-altitude mountain ranges, making the border mostly inaccessible by road and public transport. There are no formal border crossings in this region, rendering inaccessible by any means other than by foot. The mountain thus operates as an effective natural barrier to informal border crossings. The area is also a recreational area in that it houses a ski center and several hiking trails, and is so characterised by;
> high altitude mountains
> recreational area
The remote location of these areas does not necessarily mean they are not used by migrants to cross the border from Greece. As reports witness a migrant death in this area in 2015, it is safe to assume it may prove to be an active factor in the perilous journeys people take to cross borders unnoticed. It may well be that areas such as this, where mountains are made accessible through the development of ski centers etc. are the most accessible parts of a long stretch of largely inaccessible border.
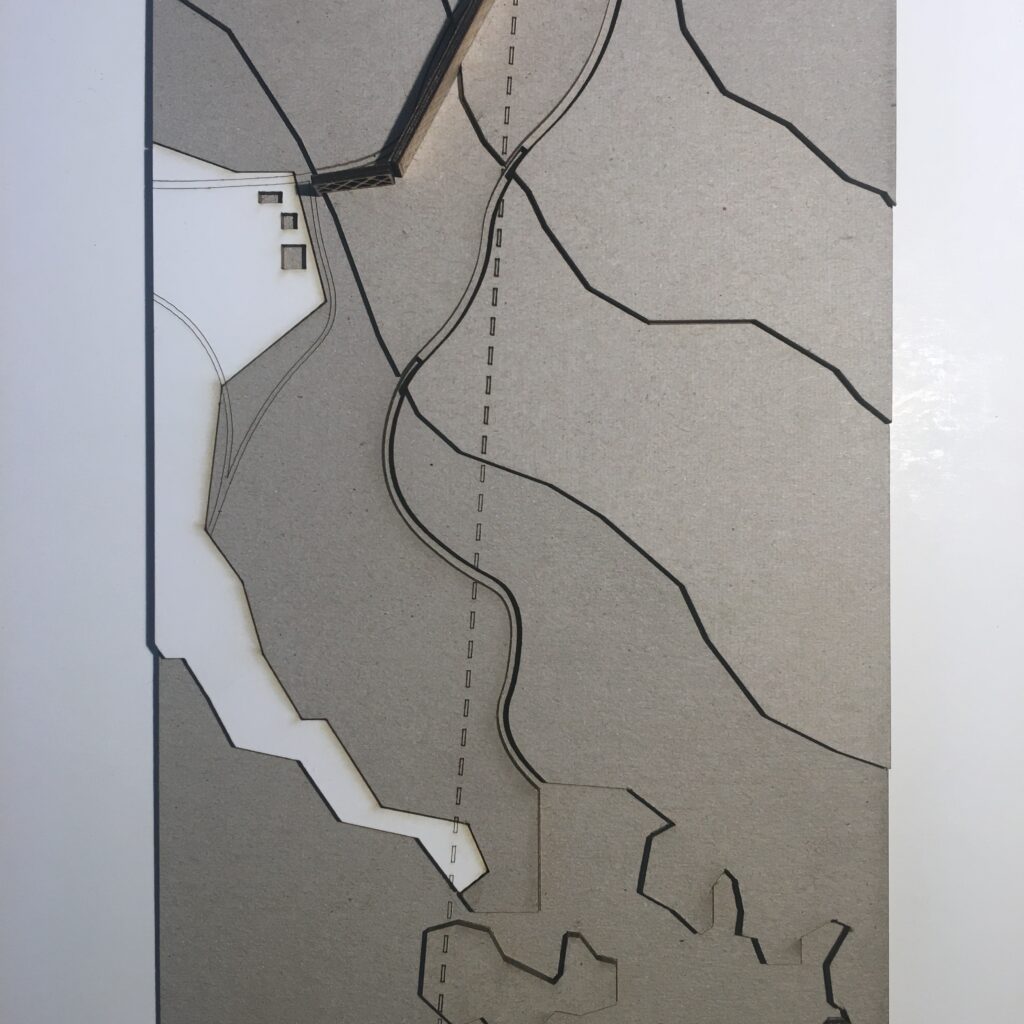
Typology 3: Border at Nicolic beach
> river/green/barrier

Observation of satellite images indicates that the border here contains two geographical types;
> river border
> green border
This border segment has also been further spatialized by the construction of a physical border barrier, a border fence. Along the fence (on the Macedonian side) runs a dirt road, probably for maintenence and potential patrols. This fence also puts the border segment into the category of separation barrier;
> separation barrier (fence)